The following program calculates the roots of a set of nonlinear equations using Newton's method.
Click here to download a ZIP file containing the project files for this program.
The program prompts you to either use the predefined default input values or to enter the following:
1. The values for the initial set of variables
2. The values for the tolerances for each variable.
3. The function tolerance
4. The maximum number of iterations
In case you choose the default input values, the program displays these values and proceeds to find the roots. In the case you select being prompted, the program displays the name of each input variable along with its default value. You can then either enter a new value or simply press Enter to use the default value. This approach allows you to quickly and efficiently change only a few input values if you so desire.
The program displays the following final results:
1. The coordinates of the minimum value.
2. The number of iterations
The current code finds the roots for the following functions:
F1(X) = X1 * X2 * X3 - 6
F2(X) = (X1 + X2) / X3 - 1
F3(X) = (X1 + 1) * X2 - X3 - 1
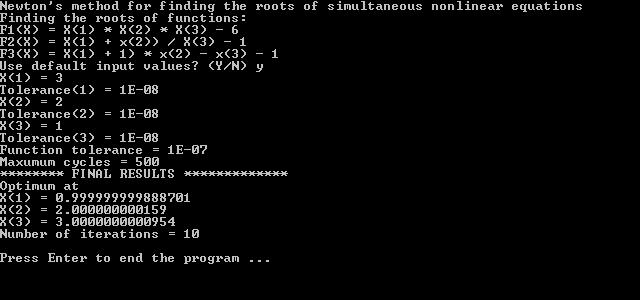
Using initial guesses of 3, 2, 1, and 1e-7 for the all variable tolerances, a function tolerance of 1e-7, and a maximum number of 500 iterations. Here is the sample console screen:

Here is the listing for the main module. The module contains several test functions:
Module Module1
Sub Main()
Dim nNumVars As Integer = 3
Dim fX() As Double = {3, 2, 1}
Dim fParam() As Double = {0, 0, 0}
Dim fToler() As Double = {0.00000001, 0.00000001, 0.00000001}
Dim nIter As Integer = 0
Dim nMaxIter As Integer = 500
Dim fEpsFx As Double = 0.0000001
Dim I As Integer
Dim sAnswer As String
Dim oRoot As CRoots_NLE_Newton1
Dim MyFx As MyFxDelegate = AddressOf Fx1
Dim SayFx As SayFxDelegate = AddressOf SayFx1
oRoot = New CRoots_NLE_Newton1
Console.WriteLine("Newton's method for finding the roots of simultaneous nonlinear equations")
Console.WriteLine("Finding the roots of functions:")
Console.WriteLine(SayFx())
Console.Write("Use default input values? (Y/N) ")
sAnswer = Console.ReadLine()
If sAnswer.ToUpper() = "Y" Then
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
Console.WriteLine("X({0}) = {1}", I + 1, fX(I))
Console.WriteLine("Tolerance({0}) = {1}", I + 1, fToler(I))
Next
Console.WriteLine("Function tolerance = {0}", fEpsFx)
Console.WriteLine("Maxumum cycles = {0}", nMaxIter)
Else
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
fX(I) = GetIndexedDblInput("X", I + 1, fX(I))
fToler(I) = GetIndexedDblInput("Tolerance", I + 1, fToler(I))
Next
fEpsFx = GetIntInput("Function tolerance", fEpsFx)
nMaxIter = GetDblInput("Maxumum cycles", nMaxIter)
End If
Console.WriteLine("******** FINAL RESULTS *************")
oRoot.CalcRoots(nNumVars, fX, fParam, fToler, fEpsFx, nMaxIter, nIter, MyFx)
Console.WriteLine("Optimum at")
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
Console.WriteLine("X({0}) = {1}", I + 1, fX(I))
Next
Console.WriteLine("Number of iterations = {0}", nIter)
Console.WriteLine()
Console.Write("Press Enter to end the program ...")
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub
Function GetDblInput(ByVal sPrompt As String, ByVal fDefInput As Double) As Double
Dim sInput As String
Console.Write("{0}? ({1}): ", sPrompt, fDefInput)
sInput = Console.ReadLine()
If sInput.Trim().Length > 0 Then
Return Double.Parse(sInput)
Else
Return fDefInput
End If
End Function
Function GetIntInput(ByVal sPrompt As String, ByVal nDefInput As Integer) As Integer
Dim sInput As String
Console.Write("{0}? ({1}): ", sPrompt, nDefInput)
sInput = Console.ReadLine()
If sInput.Trim().Length > 0 Then
Return Double.Parse(sInput)
Else
Return nDefInput
End If
End Function
Function GetIndexedDblInput(ByVal sPrompt As String, ByVal nIndex As Integer, ByVal fDefInput As Double) As Double
Dim sInput As String
Console.Write("{0}({1})? ({2}): ", sPrompt, nIndex, fDefInput)
sInput = Console.ReadLine()
If sInput.Trim().Length > 0 Then
Return Double.Parse(sInput)
Else
Return fDefInput
End If
End Function
Function GetIndexedIntInput(ByVal sPrompt As String, ByVal nIndex As Integer, ByVal nDefInput As Integer) As Integer
Dim sInput As String
Console.Write("{0}({1})? ({2}): ", sPrompt, nIndex, nDefInput)
sInput = Console.ReadLine()
If sInput.Trim().Length > 0 Then
Return Double.Parse(sInput)
Else
Return nDefInput
End If
End Function
Function SayFx1() As String
Return "F1(X) = X(1) * X(2) * X(3) - 6" & vbCrLf & _
"F2(X) = X(1) + x(2)) / X(3) - 1" & vbCrLf & _
"F3(X) = X(1) + 1) * x(2) - x(3) - 1"
End Function
Function Fx1(ByVal N As Integer, ByRef X() As Double, ByRef fParam() As Double, ByVal nVarIndex As Integer) As Double
Select Case nVarIndex
Case 1
Return X(0) * X(1) * X(2) - 6
Case 2
Return (X(0) + X(1)) / X(2) - 1
Case Else ' case 3
Return (X(0) + 1) * X(1) - X(2) - 1
End Select
End Function
End Module
Notice that the user-defined function has the following:
Please observe the following rules::
The program uses the following class to solve the simultaneous nonlinear functions along with the matrix class library (MatrixLib.vb) which you can download from the VB.Net: Master Page.
Public Delegate Function MyFxDelegate(ByVal nNumVars As Integer, ByRef fX() As Double, ByRef fParam() As Double, ByVal nVarIndex As Integer) As Double
Public Delegate Function SayFxDelegate() As String
Public Class CRoots_NLE_Newton1
Public Sub CalcRoots(ByVal nNumVars As Integer, ByRef fX() As Double, ByRef fParam() As Double, ByRef fToler() As Double, _
ByVal fEpsFx As Double, ByVal nMaxIter As Integer, ByRef nIter As Integer, ByVal MyFx As MyFxDelegate)
Dim g(nNumVars) As Double
Dim Jmat(nNumVars, nNumVars) As Double
Dim H, fXJ, Fp As Double
Dim I, J As Integer
Dim bGoOn As Boolean
nIter = 0
bGoOn = True
Do While bGoOn And nIter < nMaxIter
nIter += 1
If nIter > nMaxIter Then Exit Do
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
g(I) = MyFx(nNumVars, fX, fParam, I)
For J = 0 To nNumVars - 1
H = 0.01 * (1 + Math.Abs(fX(J)))
fXJ = fX(J)
fX(J) = fXJ + H
Fp = MyFx(nNumVars, fX, fParam, I)
fX(J) = fXJ
Jmat(I, J) = (Fp - g(I)) / H
Next
Next
' solve for the guess improvements
MatrixLibVb.SolveLU(Jmat, g, nNumVars)
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
fX(I) = fX(I) - g(I)
Next
' check refinement convergence
bGoOn = False
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
If Math.Abs(g(I)) > fToler(I) Then
bGoOn = True
End If
Next
' check function convergence
If bGoOn Then
bGoOn = False
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
If Math.Abs(g(I)) > fEpsFx Then
bGoOn = True
End If
Next
End If
Loop
End Sub
End Class
Copyright (c) Namir Shammas. All rights reserved.