The following program calculates the minimum point of a multi-variable function using the grid search method. This method performs a multi-dimensional grid search. The grid is defined by a multiple dimensions. Each dimension has a range of values. Each range is divided into a set of equal-value intervals. The multi-dimensional grid has a centroid which locates the optimum point. The search involves multiple passes. In each pass, the method local a node (point of intersection) with the least function value. This node becomes the new centroid and builds a smaller grid around it. Successive passes end up shrinking the multidimensional grid around the optimum.
Click here to download a ZIP file containing the project files for this program.
The program prompts you to either use the predefined default input values or to enter the following for each variable (i.e. dimension):
1. The values that define the lower and upper limits of a search range for a variable,
2. The number of divisions for a range.
3. The minimum range value, used to determine when to stop searching..
The program also asks you to enter the function tolerance. The program uses this value to possible stop iterating when successive best function values are close enough.
In case you choose the default input values, the program displays these values and proceeds to find the optimum point. In the case you select being prompted, the program displays the name of each input variable along with its default value. You can then either enter a new value or simply press Enter to use the default value. This approach allows you to quickly and efficiently change only a few input values if you so desire.
The program displays the following final results:
1. The coordinates of the minimum point.
2. The minimum function value.
3. The number of iterations
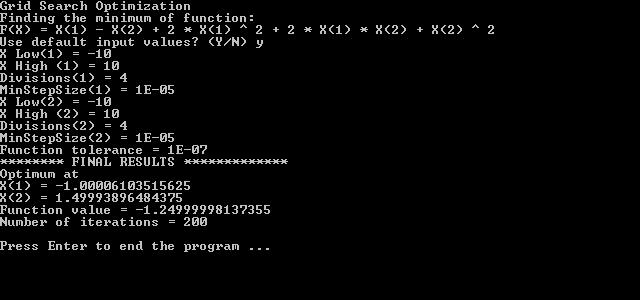
Here is a sample session to find the minimum of function:
f(x) = x1 - x2 + 2 * x1 ^ 2 + 2 * x1 * x2 + x2 ^ 2
Using, for each variable, the range of (-10, 10), initial range divisions of 4, minimum step size of 1e-5. The solution also uses a function tolerance of 1e-7. Here is the sample console screen:

Here is the listing for the main module. The module contains several test functions:
Module Module1
Sub Main()
Dim nNumVars As Integer = 2
Dim fX() As Double = {0, 0}
Dim fParam() As Double = {0, 0}
Dim fXLo() As Double = {-10, -10}
Dim fXHi() As Double = {10, 10}
Dim nNumDiv() As Integer = {4, 4}
Dim fMinDeltaX() As Double = {0.00001, 0.00001}
Dim nIter As Integer = 0
Dim fEpsFx As Double = 0.0000001
Dim I As Integer
Dim fBestF
Dim sAnswer As String
Dim oOpt As CGridSearch
Dim MyFx As MyFxDelegate = AddressOf Fx3
Dim SayFx As SayFxDelegate = AddressOf SayFx3
oOpt = New CGridSearch
Console.WriteLine("Grid Search Optimization")
Console.WriteLine("Finding the minimum of function:")
Console.WriteLine(SayFx())
Console.Write("Use default input values? (Y/N) ")
sAnswer = Console.ReadLine()
If sAnswer.ToUpper() = "Y" Then
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
Console.WriteLine("X Low({0}) = {1}", I + 1, fXLo(I))
Console.WriteLine("X High ({0}) = {1}", I + 1, fXHi(I))
Console.WriteLine("Divisions({0}) = {1}", I + 1, nNumDiv(I))
Console.WriteLine("MinStepSize({0}) = {1}", I + 1, fMinDeltaX(I))
Next
Console.WriteLine("Function tolerance = {0}", fEpsFx)
Else
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
fXLo(I) = GetIndexedDblInput("X low", I + 1, fXLo(I))
fXHi(I) = GetIndexedDblInput("X high", I + 1, fXHi(I))
nNumDiv(I) = GetIndexedIntInput("Number of divisions", I + 1, nNumDiv(I))
fMinDeltaX(I) = GetIndexedDblInput("Minimum step size", I + 1, fMinDeltaX(I))
Next
fEpsFx = GetDblInput("Function tolerance", fEpsFx)
End If
Console.WriteLine("******** FINAL RESULTS *************")
fBestF = oOpt.CalcOptim(nNumVars, fX, fParam, fXLo, fXHi, nNumDiv, fMinDeltaX, fEpsFx, nIter, MyFx)
Console.WriteLine("Optimum at")
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
Console.WriteLine("X({0}) = {1}", I + 1, fX(I))
Next
Console.WriteLine("Function value = {0}", fBestF)
Console.WriteLine("Number of iterations = {0}", nIter)
Console.WriteLine()
Console.Write("Press Enter to end the program ...")
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub
Function GetDblInput(ByVal sPrompt As String, ByVal fDefInput As Double) As Double
Dim sInput As String
Console.Write("{0}? ({1}): ", sPrompt, fDefInput)
sInput = Console.ReadLine()
If sInput.Trim().Length > 0 Then
Return Double.Parse(sInput)
Else
Return fDefInput
End If
End Function
Function GetIntInput(ByVal sPrompt As String, ByVal nDefInput As Integer) As Integer
Dim sInput As String
Console.Write("{0}? ({1}): ", sPrompt, nDefInput)
sInput = Console.ReadLine()
If sInput.Trim().Length > 0 Then
Return Double.Parse(sInput)
Else
Return nDefInput
End If
End Function
Function GetIndexedDblInput(ByVal sPrompt As String, ByVal nIndex As Integer, ByVal fDefInput As Double) As Double
Dim sInput As String
Console.Write("{0}({1})? ({2}): ", sPrompt, nIndex, fDefInput)
sInput = Console.ReadLine()
If sInput.Trim().Length > 0 Then
Return Double.Parse(sInput)
Else
Return fDefInput
End If
End Function
Function GetIndexedIntInput(ByVal sPrompt As String, ByVal nIndex As Integer, ByVal nDefInput As Integer) As Integer
Dim sInput As String
Console.Write("{0}({1})? ({2}): ", sPrompt, nIndex, nDefInput)
sInput = Console.ReadLine()
If sInput.Trim().Length > 0 Then
Return Double.Parse(sInput)
Else
Return nDefInput
End If
End Function
Function SayFx1() As String
Return "F(X) = 10 + (X(1) - 2) ^ 2 + (X(2) + 5) ^ 2"
End Function
Function Fx1(ByVal N As Integer, ByRef X() As Double, ByRef fParam() As Double) As Double
Return 10 + (X(0) - 2) ^ 2 + (X(1) + 5) ^ 2
End Function
Function SayFx2() As String
Return "F(X) = 100 * (X(1) - X(2) ^ 2) ^ 2 + (X(2) - 1) ^ 2"
End Function
Function Fx2(ByVal N As Integer, ByRef X() As Double, ByRef fParam() As Double) As Double
Return 100 * (X(0) - X(1) ^ 2) ^ 2 + (X(1) - 1) ^ 2
End Function
Function SayFx3() As String
Return "F(X) = X(1) - X(2) + 2 * X(1) ^ 2 + 2 * X(1) * X(2) + X(2) ^ 2"
End Function
Function Fx3(ByVal N As Integer, ByRef X() As Double, ByRef fParam() As Double) As Double
Return X(0) - X(1) + 2 * X(0) ^ 2 + 2 * X(0) * X(1) + X(1) ^ 2
End Function
End Module
Notice that the user-defined functions have accompanying helper functions to display the mathematical expression of the function being optimized. For example, function Fx1 has the helper function SayFx1 to list the function optimized in Fx1. Please observe the following rules::
The program uses the following class to optimize the objective function:
Public Delegate Function MyFxDelegate(ByVal nNumVars As Integer, ByRef fX() As Double, ByRef fParam() As Double) As Double
Public Delegate Function SayFxDelegate() As String
Public Class CGridSearch
Public Function CalcOptim(ByVal nNumVars As Integer, ByRef fXCenter() As Double, ByRef fParam() As Double, _
ByRef fXLo() As Double, ByRef fXHi() As Double, ByRef nNumDiv() As Integer, _
ByRef fMinDeltaX() As Double, ByVal fEpsFx As Double, ByRef nIter As Integer, _
ByVal MyFx As MyFxDelegate) As Double
Dim fDeltaX(), fX(), fBestX() As Double
Dim F, fBestF, fLastBestF As Double
Dim I As Integer
Dim bGoOn As Boolean
ReDim fDeltaX(nNumVars), fX(nNumVars), fBestX(nNumVars)
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
fXCenter(I) = (fXLo(I) + fXHi(I)) / 2
fBestX(I) = fXCenter(I)
fDeltaX(I) = (fXHi(I) - fXLo(I)) / nNumDiv(I)
fX(I) = fXLo(I)
Next
' calculate and display function value at initial point
fBestF = MyFx(nNumVars, fXCenter, fParam)
If fBestF > 0 Then
fLastBestF = 100 + fBestF
Else
fLastBestF = 100 - fBestF
End If
nIter = 0
Do
Do
nIter += 1
F = MyFx(nNumVars, fX, fParam)
If F < fBestF Then
fLastBestF = fBestF
fBestF = F
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
fBestX(I) = fX(I)
Next I
End If
'*****************************************************
' The next For loop implements a programming tricks
' that simulated nested loops using just one For loop
'*****************************************************
' search next grid node
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
If fX(I) >= fXHi(I) Then
If I < (nNumVars - 1) Then
fX(I) = fXLo(I)
Else
Exit Do
End If
Else
fX(I) += fDeltaX(I)
Exit For
End If
Next I
Loop
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
fXCenter(I) = fBestX(I)
fDeltaX(I) = fDeltaX(I) / nNumDiv(I)
fXLo(I) = fXCenter(I) - fDeltaX(I) * nNumDiv(I) / 2
fXHi(I) = fXCenter(I) + fDeltaX(I) * nNumDiv(I) / 2
fX(I) = fXLo(I) ' set initial fX
Next I
' fBestF = MyFx(XCenter, N)
bGoOn = False
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
If fDeltaX(I) > fMinDeltaX(I) Then bGoOn = True
Next I
bGoOn = bGoOn And (Math.Abs(fBestF - fLastBestF) > fEpsFx)
Loop While bGoOn
Return fBestF
End Function
End Class
Copyright (c) Namir Shammas. All rights reserved.