The following program calculates the minimum point of a multi-variable function using the Conjugate Gradient (Fletcher-Reeves) method.
Click here to download a ZIP file containing the project files for this program.
The program prompts you to either use the predefined default input values or to enter the following :
1. The coordinates of the minimum value.
2. The minimum function value.
3. The maximum number of iterations
In case you choose the default input values, the program displays these values and proceeds to find the optimum point. In the case you select being prompted, the program displays the name of each input variable along with its default value. You can then either enter a new value or simply press Enter to use the default value. This approach allows you to quickly and efficiently change only a few input values if you so desire.
The program displays the following final results:
1. The coordinates of the minimum value.
2. The minimum function value.
3. The number of iterations
The current code finds the minimum for the following function:
f(x1,x2) = x1 - x2 + 2 * x1 ^ 2 + 2 * x1 * x2 + x2 ^ 2
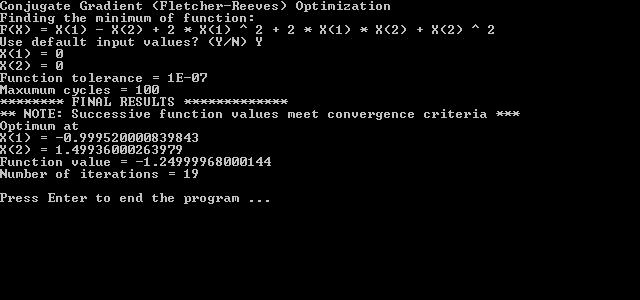
Using an initial value of 0 for each variable, a function tolerance of 1e-7, and a maximum number of 100 search cycles. Here is the sample console screen:

Here is the listing for the main module. The module contains several test functions:
Module Module1
Sub Main()
Dim nNumVars As Integer = 2
Dim fX() As Double = {0, 0}
Dim fParam() As Double = {0, 0}
Dim nIter As Integer = 0
Dim nMaxIter As Integer = 100
Dim fEpsFx As Double = 0.0000001
Dim I As Integer
Dim fBestF As Double
Dim sAnswer As String, sErrorMsg As String = ""
Dim oOpt As CConjugateGradient1
Dim MyFx As MyFxDelegate = AddressOf Fx3
Dim SayFx As SayFxDelegate = AddressOf SayFx3
oOpt = New CConjugateGradient1
Console.WriteLine("Conjugate Gradient (Fletcher-Reeves) Optimization")
Console.WriteLine("Finding the minimum of function:")
Console.WriteLine(SayFx())
Console.Write("Use default input values? (Y/N) ")
sAnswer = Console.ReadLine()
If sAnswer.ToUpper() = "Y" Then
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
Console.WriteLine("X({0}) = {1}", I + 1, fX(I))
Next
Console.WriteLine("Function tolerance = {0}", fEpsFx)
Console.WriteLine("Maxumum cycles = {0}", nMaxIter)
Else
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
fX(I) = GetIndexedDblInput("X", I + 1, fX(I))
Next
fEpsFx = GetDblInput("Function tolerance", fEpsFx)
nMaxIter = GetDblInput("Maxumum cycles", nMaxIter)
End If
Console.WriteLine("******** FINAL RESULTS *************")
fBestF = oOpt.CalcOptim(nNumVars, fX, fParam, fEpsFx, nMaxIter, nIter, sErrorMsg, MyFx)
If sErrorMsg.Length > 0 Then
Console.WriteLine("** NOTE: {0} ***", sErrorMsg)
End If
Console.WriteLine("Optimum at")
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
Console.WriteLine("X({0}) = {1}", I + 1, fX(I))
Next
Console.WriteLine("Function value = {0}", fBestF)
Console.WriteLine("Number of iterations = {0}", nIter)
Console.WriteLine()
Console.Write("Press Enter to end the program ...")
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub
Function GetDblInput(ByVal sPrompt As String, ByVal fDefInput As Double) As Double
Dim sInput As String
Console.Write("{0}? ({1}): ", sPrompt, fDefInput)
sInput = Console.ReadLine()
If sInput.Trim().Length > 0 Then
Return Double.Parse(sInput)
Else
Return fDefInput
End If
End Function
Function GetIntInput(ByVal sPrompt As String, ByVal nDefInput As Integer) As Integer
Dim sInput As String
Console.Write("{0}? ({1}): ", sPrompt, nDefInput)
sInput = Console.ReadLine()
If sInput.Trim().Length > 0 Then
Return Double.Parse(sInput)
Else
Return nDefInput
End If
End Function
Function GetIndexedDblInput(ByVal sPrompt As String, ByVal nIndex As Integer, ByVal fDefInput As Double) As Double
Dim sInput As String
Console.Write("{0}({1})? ({2}): ", sPrompt, nIndex, fDefInput)
sInput = Console.ReadLine()
If sInput.Trim().Length > 0 Then
Return Double.Parse(sInput)
Else
Return fDefInput
End If
End Function
Function GetIndexedIntInput(ByVal sPrompt As String, ByVal nIndex As Integer, ByVal nDefInput As Integer) As Integer
Dim sInput As String
Console.Write("{0}({1})? ({2}): ", sPrompt, nIndex, nDefInput)
sInput = Console.ReadLine()
If sInput.Trim().Length > 0 Then
Return Double.Parse(sInput)
Else
Return nDefInput
End If
End Function
Function SayFx1() As String
Return "F(X) = 10 + (X(1) - 2) ^ 2 + (X(2) + 5) ^ 2"
End Function
Function Fx1(ByVal N As Integer, ByRef X() As Double, ByRef fParam() As Double) As Double
Return 10 + (X(0) - 2) ^ 2 + (X(1) + 5) ^ 2
End Function
Function SayFx2() As String
Return "F(X) = 100 * (X(1) - X(2) ^ 2) ^ 2 + (X(2) - 1) ^ 2"
End Function
Function Fx2(ByVal N As Integer, ByRef X() As Double, ByRef fParam() As Double) As Double
Return 100 * (X(0) - X(1) ^ 2) ^ 2 + (X(1) - 1) ^ 2
End Function
Function SayFx3() As String
Return "F(X) = X(1) - X(2) + 2 * X(1) ^ 2 + 2 * X(1) * X(2) + X(2) ^ 2"
End Function
Function Fx3(ByVal N As Integer, ByRef X() As Double, ByRef fParam() As Double) As Double
Return X(0) - X(1) + 2 * X(0) ^ 2 + 2 * X(0) * X(1) + X(1) ^ 2
End Function
' X(0) - X(1) + 2 * X(0) ^ 2 + 2 * X(0) * X(1) + X(1) ^ 2
End Module
Notice that the user-defined functions have accompanying helper functions to display the mathematical expression of the function being optimized. For example, function Fx1 has the helper function SayFx1 to list the function optimized in Fx1. Please observe the following rules::
The program uses the following class to optimize the objective function:
Public Delegate Function MyFxDelegate(ByVal nNumVars As Integer, ByRef fX() As Double, ByRef fParam() As Double) As Double
Public Delegate Function SayFxDelegate() As String
Public Class CConjugateGradient1
Dim m_MyFx As MyFxDelegate
Function MyFxEx(ByVal nNumVars As Integer, _
ByRef fX() As Double, ByRef fParam() As Double, _
ByRef fDeltaX() As Double, ByVal fLambda As Double) As Double
Dim I As Integer
Dim fXX(nNumVars) As Double
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
fXX(I) = fX(I) + fLambda * fDeltaX(I)
Next I
MyFxEx = m_MyFx(nNumVars, fXX, fParam)
End Function
Private Sub GetGradients( _
ByVal nNumVars As Integer, ByRef fX() As Double, ByRef fParam() As Double, _
ByRef fDeriv() As Double, ByRef fDerivNorm As Double)
Dim I As Integer
Dim fXX, H, Fp, Fm As Double
fDerivNorm = 0
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
fXX = fX(I)
H = 0.01 * (1 + Math.Abs(fXX))
fX(I) = fXX + H
Fp = m_MyFx(nNumVars, fX, fParam)
fX(I) = fXX - H
Fm = m_MyFx(nNumVars, fX, fParam)
fX(I) = fXX
fDeriv(I) = (Fp - Fm) / 2 / H
fDerivNorm += fDeriv(I) ^ 2
Next I
fDerivNorm = Math.Sqrt(fDerivNorm)
End Sub
Function LinSearch_DirectSearch(ByVal nNumVars As Integer, ByRef fX() As Double, ByRef fParam() As Double, _
ByRef fLambda As Double, ByRef fDeltaX() As Double, ByVal InitStep As Double, _
ByVal MinStep As Double) As Boolean
Dim F1, F2 As Double
F1 = MyFxEx(nNumVars, fX, fParam, fDeltaX, fLambda)
Do
F2 = MyFxEx(nNumVars, fX, fParam, fDeltaX, fLambda + InitStep)
If F2 < F1 Then
F1 = F2
fLambda += InitStep
Else
F2 = MyFxEx(nNumVars, fX, fParam, fDeltaX, fLambda - InitStep)
If F2 < F1 Then
F1 = F2
fLambda -= InitStep
Else
' reduce search step size
InitStep /= 10
End If
End If
Loop Until InitStep < MinStep
Return True
End Function
Public Function CalcOptim(ByVal nNumVars As Integer, ByRef fX() As Double, ByRef fParam() As Double, _
ByVal fEpsFx As Double, ByVal nMaxIter As Integer, _
ByRef nIter As Integer, ByRef sErrorMsg As String, _
ByVal MyFx As MyFxDelegate) As Double
Dim I As Integer
Dim fDeriv(nNumVars) As Double, fDerivOld(nNumVars) As Double
Dim F, fDFNorm, fDFNormOld As Double
Dim fLambda, fLastF As Double
m_MyFx = MyFx
' calculate and function value at initial point
fLastF = MyFx(nNumVars, fX, fParam)
GetGradients(nNumVars, fX, fParam, fDeriv, fDFNorm)
fLambda = 0
If LinSearch_DirectSearch(nNumVars, fX, fParam, fLambda, fDeriv, 0.1, 0.000001) Then
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
fX(I) += fLambda * fDeriv(I)
Next I
Else
sErrorMsg = "Failed linear search"
Return fLastF
End If
nIter = 1
Do
nIter += 1
If nIter > nMaxIter Then
sErrorMsg = "Reached maximum iterations limit"
Exit Do
End If
fDFNormOld = fDFNorm
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
fDerivOld(I) = fDeriv(I) ' save old gradient
Next I
GetGradients(nNumVars, fX, fParam, fDeriv, fDFNorm)
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
fDeriv(I) = (fDFNorm / fDFNormOld) ^ 2 * fDerivOld(I) - fDeriv(I)
Next I
If fDFNorm <= fEpsFx Then
sErrorMsg = "Gradient norm meets convergence criteria"
Exit Do
End If
' For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
' fDeriv(I) = -fDeriv(I) / fDFNorm
' Next I
fLambda = 0
' If LinSearch_Newton(fX, nNumVars, fLambda, fDeriv, 0.0001, 100) Then
If LinSearch_DirectSearch(nNumVars, fX, fParam, fLambda, fDeriv, 0.1, 0.000001) Then
For I = 0 To nNumVars - 1
fX(I) += fLambda * fDeriv(I)
Next I
F = MyFx(nNumVars, fX, fParam)
If Math.Abs(F - fLastF) < fEpsFx Then
sErrorMsg = "Successive function values meet convergence criteria"
Exit Do
Else
fLastF = F
End If
Else
sErrorMsg = "Failed linear search"
Exit Do
End If
Loop
Return fLastF
End Function
End Class
Copyright (c) Namir Shammas. All rights reserved.